Components
- Wemos ESP-WROOM-32
- Micro USB to USB cable
Setup Your Environment
Arduino IDE
- Install the Arduino IDE (Integrated development environment). You can download it for Mac OS X, Windows and Linux here.
Detailed instructions can be found below:
- Installing the Arduino IDE for Windows
- Installing the Arduino IDE for Mac
- Installing the Arduino IDE for Linux
Installing the board definitions
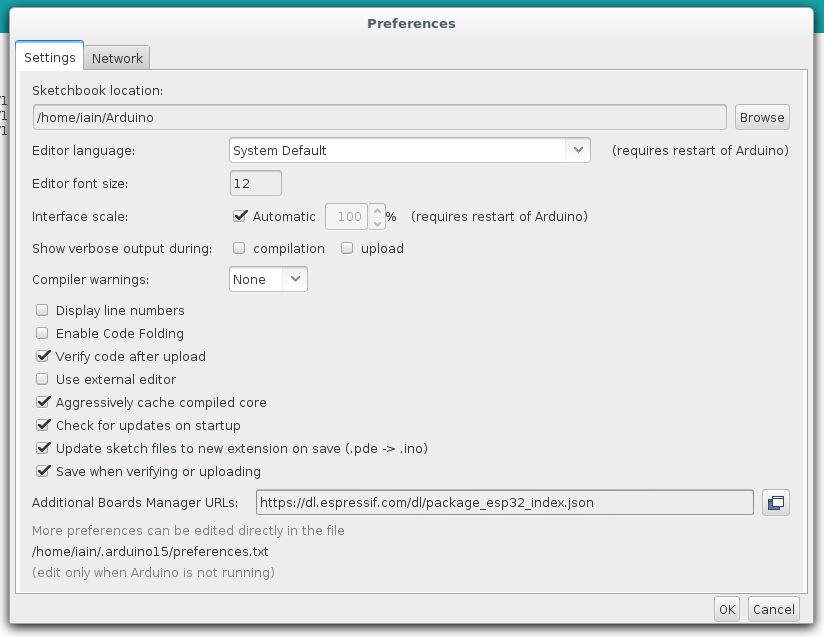
- Start the Arduino application and open
Preferences - Enter
https://dl.espressif.com/dl/package_esp32_index.jsoninto theAdditional Board Manager URLsfield. If you need more than one, they can be separated with commas
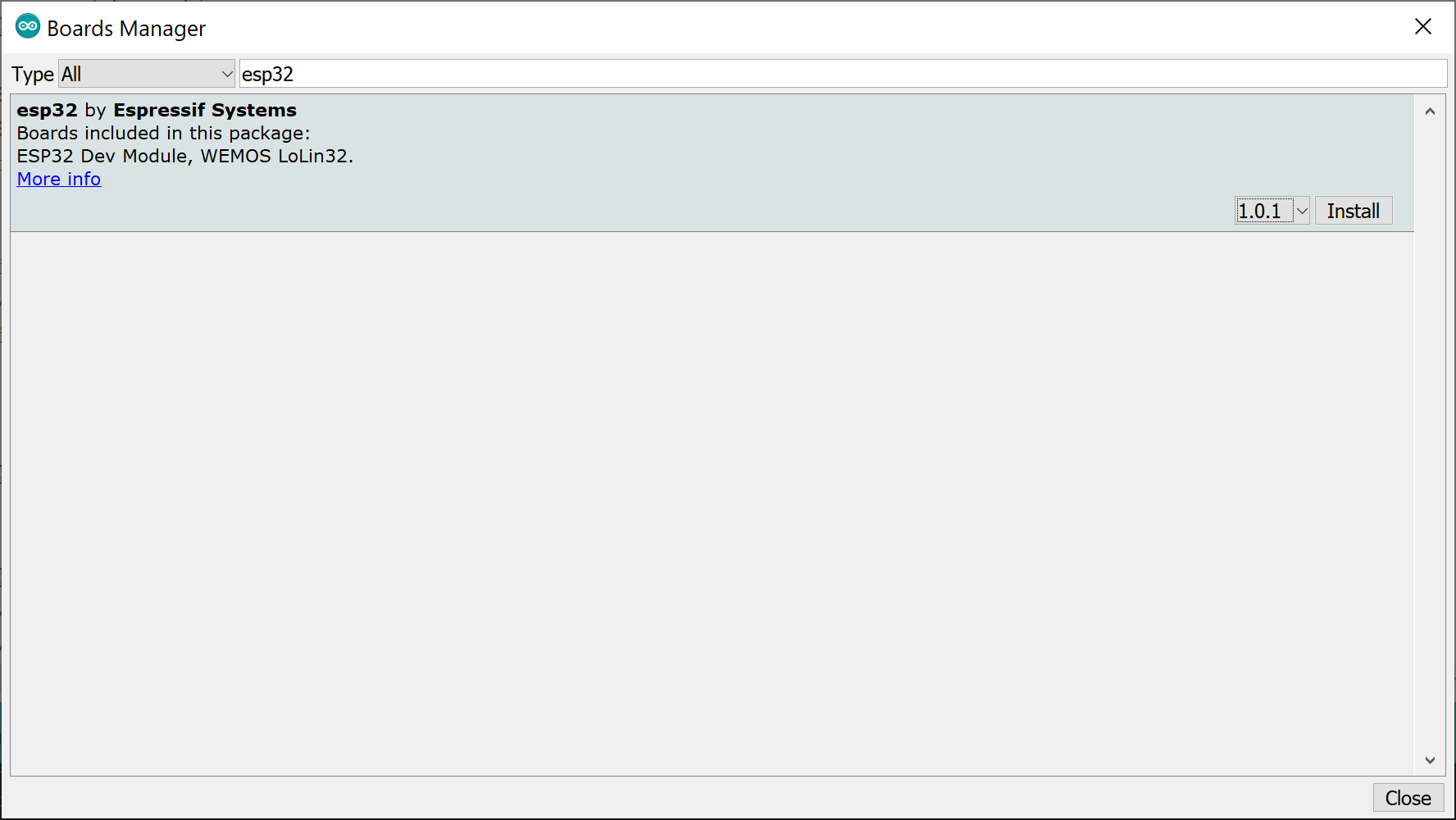
- Go to
Tools > Board > Boards Manager - Search for
esp32. - When found, select version
1.0.1and clickInstall
Our sketches do not compile successfully with ESP32 Board libraries higher than 1.0.1. Therefore it is recommended to use 1.0.1.
Selecting the board and port
The board has an On/Off Switch so make sure it's on before continuing any further
Once you've got it connected to your computer, get the name of your device's port using one of the following steps:
FTDI Drivers allow for communication between your operating system and your deviceover USB. Installing them may require Administrative privilages.
Linux and Mac OS X
- Download and install the FTDI drivers from <a href="https://www.silabs.com/products/development-tools/software/usb-to-uart-bridge-vcp-drivers"target="_blank">here. Select the appropriate version for your operating system and architecture.
- Open a terminal window and run the command `ls /dev/tty*
- Look for a device with the name that begins with
/dev/ttye.g./dev/tty.usbmodemPy343431on MAC or/dev/ttyUSB0/dev/ttyACM0on Linux.
Windows
- Download and install the FTDI drivers from <a href="https://www.silabs.com/products/development-tools/software/usb-to-uart-bridge-vcp-drivers"target="_blank">here. Select the appropriate version for your operating system and architecture.
- Open the Windows start menu and search for
Device Manager - The COM port for the Pycom device will be listed as
USB Serial Deviceor something similar - Keep note of the COM port (e.g. COM4)
Install the required libraries
- In the Arduino IDE, Go to
Sketch > Include Libraries > Manage Libraries
Install each of the following libraries by searching for their name in the search bar within the modal. A button will appear in the bottom right of the box that will allow you to install the library.
- WiFi
- ArduinoHttpClient
- ArduinoJson
Create the Sketch
- Click on
File > Newto create a new Sketch. - Copy and paste the publish event example code below in place of the empty
setup()andloop()functions
const char* ssid = "your-ssid"; // Your WiFi ssidconst char* password = "your-password"; //Your Wifi password// Get this sccret key from the wia dashboard. It should start with `d_sk`const char* device_secret_key = "your-device-secret-key";// Wia API parameterschar server[] = "api.wia.io";char path[] = "/v1/events";int port = 80;WiFiClient client;int status = WL_IDLE_STATUS;StaticJsonDocument<200> jsonBuffer;HttpClient httpClient = HttpClient(client, server, port);JsonObject root = jsonBuffer.to<JsonObject>();void setup() { // initialize serial communications and wait for port to open: Serial.begin(115200); while (!Serial) { ; // wait for serial port to connect. Needed for native USB port only } WiFi.begin(ssid, password); Serial.print("Attempting to connect to SSID: "); Serial.print(ssid); // attempt to connect to WiFi network: while (WiFi.status() != WL_CONNECTED) { Serial.print("."); // Connect to WPA/WPA2 network. // wait 5 seconds for connection: delay(5000); } Serial.print("IP address: "); Serial.println(WiFi.localIP()); Serial.println("connecting...");}// Loop function runs continuouslyvoid loop() { root["name"] = "hello-wia"; root["data"] = ""; // if you get a connection, report back via serial: if (client.connect(server, port)) { sendToWia(root); } else { // if you didn't get a connection to the server: Serial.println("connection failed"); } delay(3000); // Wait for 3 seconds to post again}// Adds the correct headers for HTTP and sends Data to Wiavoid sendToWia(JsonObject& data) { String dataStr = ""; serializeJson(data, dataStr); httpClient.beginRequest(); httpClient.post(path); httpClient.sendHeader("Content-Type", "application/json"); httpClient.sendHeader("Content-Length", dataStr.length()); httpClient.sendHeader("Authorization", "Bearer " + String(device_secret_key)); httpClient.beginBody(); httpClient.print(dataStr); httpClient.endRequest();}Replace the following values of the following variables names (Place the correct value between the quotation marks right of the variable names in the code):
ssid- with your WiFi network name.password- with your WiFi network password.device_secret_keywith your device secret key from the Wia Dashboard (the one that begins withd_sk).
Selecting Board and Port in the Arduino IDE
- Select the
Wemos Lollin 32board type by going toTools > Board - Select the port that matches from above
Check that Upload Speed is set to 115200
Upload the code
- Go to
Sketch > Uploadto send it to your ESP-WROOM-32 .
Viewing your output
- Click on button on the right hand of the screen to view your Serial monitor (Denoted in image below)
- Make sure the baud rate is set to
1152000(Shown in red rectangle in image below)
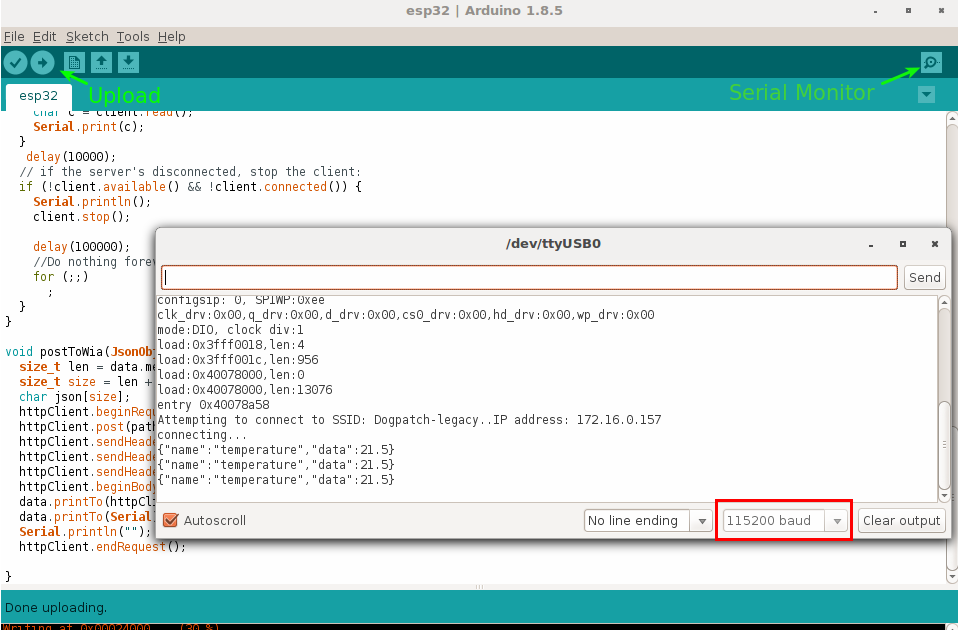
If the Serial monitor doesn't show you connecting to a WiFi, You may need to push the RST(Reset) button to run the code on the board.
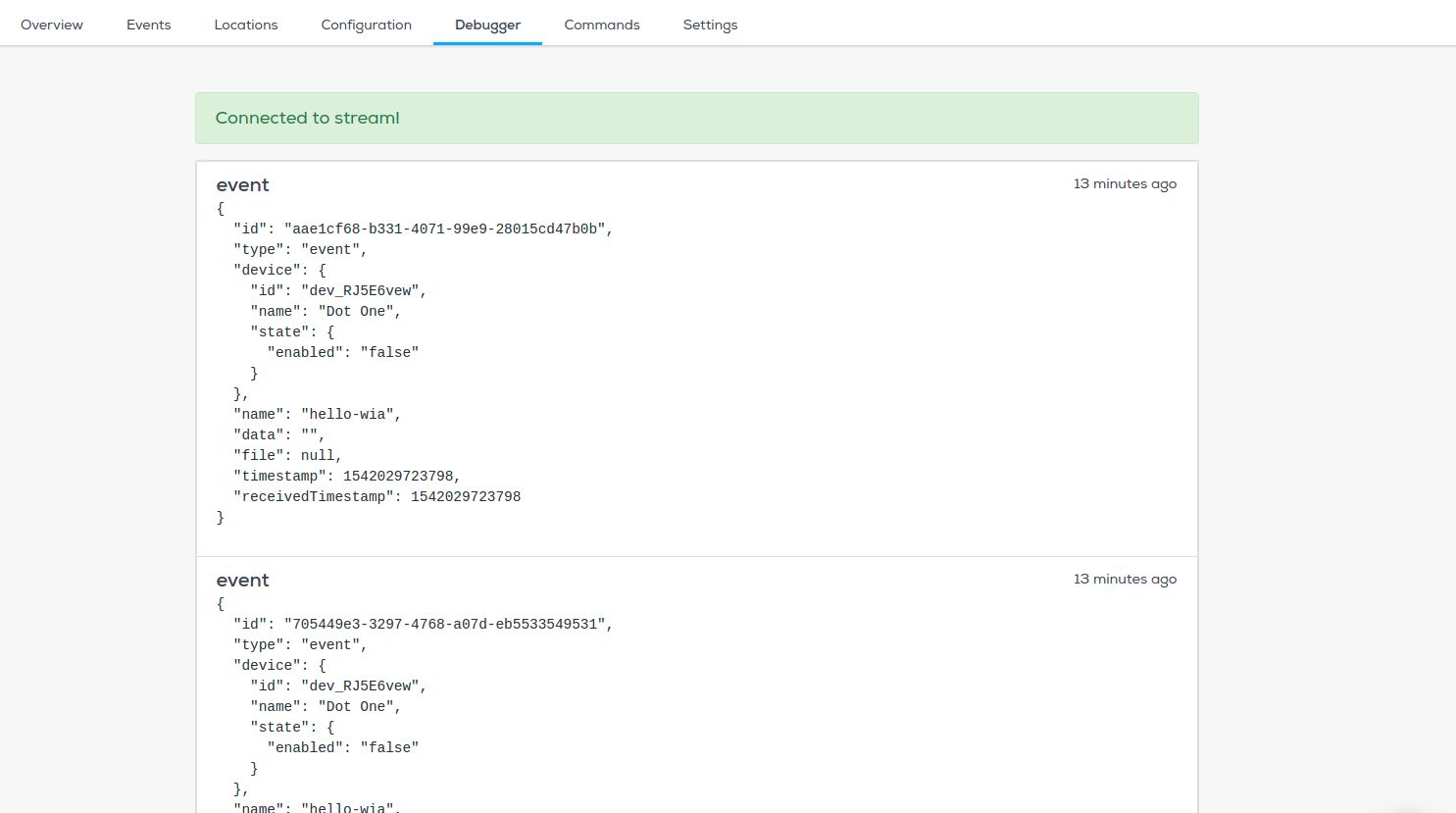
Now go to your device in the Wia dashboard and you should see the data appearing in the debugger.
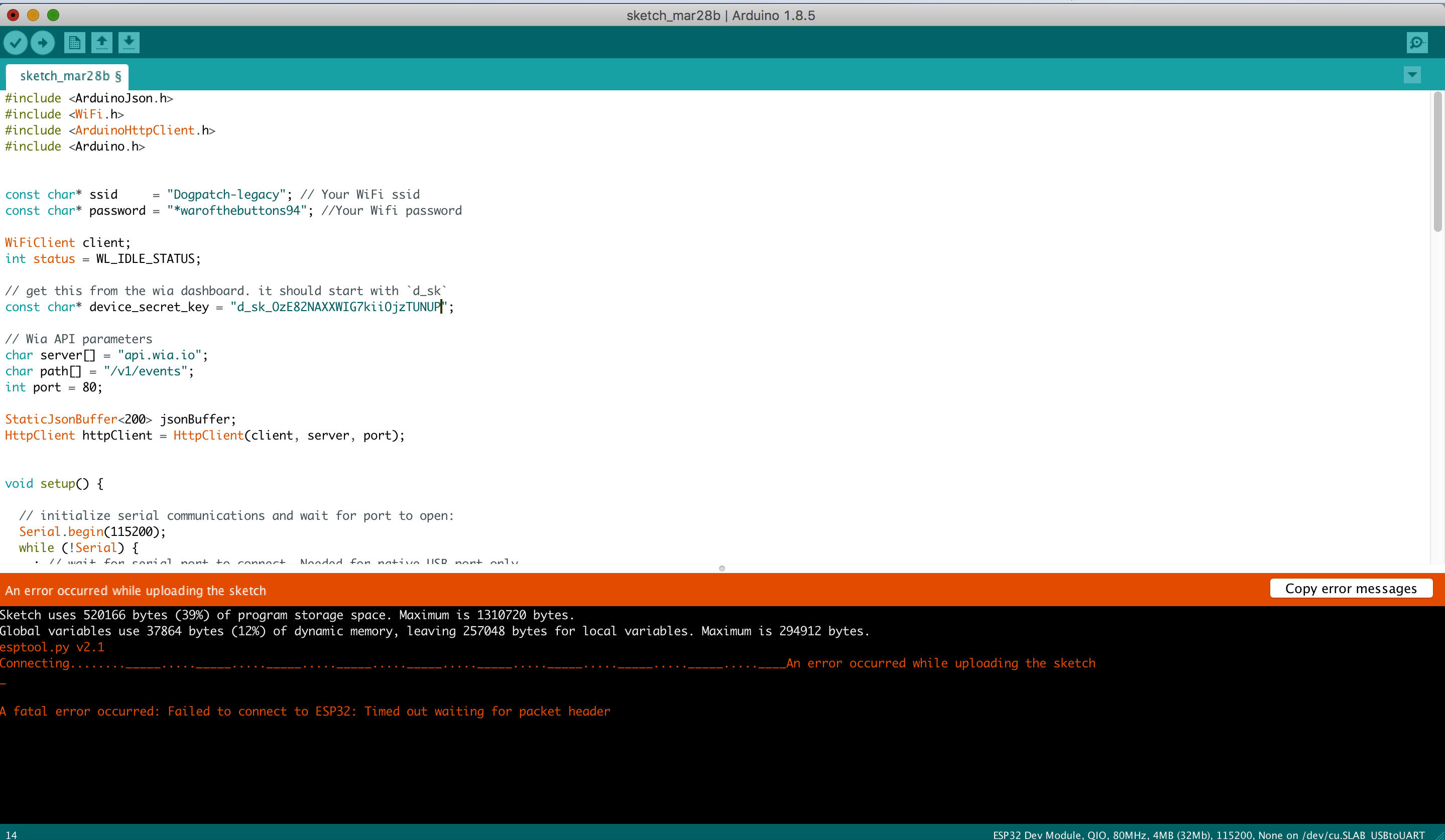
Common errors
If you encounter an error like the one denoted in the image below, check if your board and port are correctly set in the Tools menu