Components
- Any Pycom board that supports the connection through Wifi
- Pycom Pytrack board
- Micro USB to USB cable
Setup Your Development Environment
We'll be using Atom as our development environment. You can download the latest version from here. Once you've got it setup, install the Pymakr plugin. Follow the steps in this tutorial to get it setup.
Pytrack and Pysense will work out of the box for Windows 8/10/+, Mac OS as well as Linux. If using Windows 7, drivers to support the boards will need to be installed. You can find them here .
Connect to the Board
- Before connecting your module to the PyTrack board, you should update the firmware on the PyTrack. Instructions on how to do this can be found here
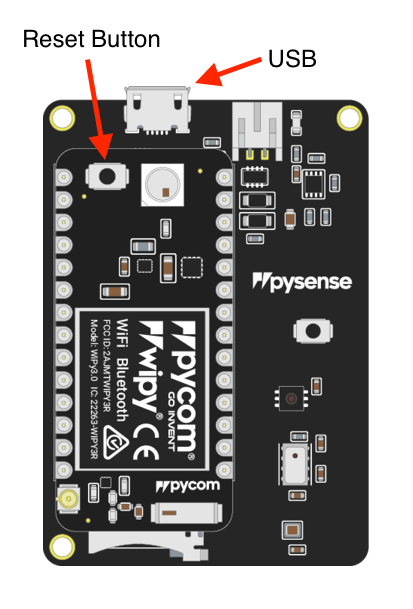
- Look for the reset button on the module (located at a corner of the board, next to the LED)
- Locate the USB connector on the PyTrack
- Insert the module on the PyTrack with the reset button pointing towards the USB connector. It * should firmly click into place and the pins should now no longer be visible.
- Connect the USB port on Pytrack board to the USB port on the computer
Get Device Name
Once you've got it connected to your computer, get the name of your device using one of the following steps:
Linux and Mac OS X
- Download and install the FTDI drivers from here. Select the appropriate version for your operating system and architecture.
- Open a terminal window and run the command
ls /dev/tty* - Look for a device with the name that begins with
/dev/ttye.g./dev/tty.usbmodemPy343431on MAC or/dev/ttyUSB0/dev/ttyACM0on Linux.
For Linux, you may need to run the two commands below. Once you've completed that, reboot your computer. This will add permissions that will allow you to upload a sketch to the board.
sudo usermod -a -G tty ${USER}
sudo usermod -a -G dialout ${USER}
Windows
- Download and install the FTDI drivers from here. Select the appropriate version for your operating system and architecture.
- Open the Windows start menu and search for 'Device Manager'
- The COM port for the Pycom device will be listed as 'USB Serial Device' or something similar
- Keep note of the COM port (e.g. COM4)
Setup Your Project
- Create a new folder for your project. I'm going to call mine
pycom-pytrack. - In Atom, go to
File > New Windowto open a new window. - Add your newly created folder by clicking File > Add Project Folder and navigating to it.
- If the Pymakr plugin is not open at the bottom of your Atom window, click on the arrow on the right hand side to open it.
- Select
Settings > ProjectSettings. In theaddressfield replace the value with the device name from the step above e.g./dev/tty.usbmodemPy343431(Mac OS X),COM3(Windows),/dev/ttyACM0(Linux) then save the file.
Add required Libraries
- Right click on the folder name in Atom and click Add Folder. Enter
libas the folder name - Right click on the
libfolder and click New File. Enterurequests.pyas the file name - Click on the file then copy and paste the code from here into that file then save it.
- For pytrack, additional libraries must also be added to the lib folder, these can be found here
Publish A Location
- In Atom, right click on your project and click New File. Enter
boot.pyas the filename. - Copy and paste the code below into the file.
from machine import UARTimport machineimport osuart = UART(0, baudrate=115200)os.dupterm(uart)machine.main('main.py')- Right click on your project and click New File. Enter
main.pyas the filename. - Copy and paste the code below into the file.
from network import WLANfrom pytrack import Pytrackimport urequests as requestsfrom L76GNSS import L76GNSSimport socketimport timeimport pycompy = Pytrack()gps = L76GNSS(py, timeout=30)# Your WiFi network credentialsWIFI_SSID = '' WIFI_KEY = ''# Get this from the Wia dashboardDEVICE_SECRET_KEY = 'your-device-secret-key'# Delay between each eventDELAY = 30wlan = WLAN(mode=WLAN.STA)nets = wlan.scan()# Connect to the WiFi networkfor net in nets: if net.ssid == WIFI_SSID: print('Network found!') wlan.connect(net.ssid, auth=(net.sec, WIFI_KEY), timeout=5000) print('Connecting...') while not wlan.isconnected(): machine.idle() # save power while waiting print('WLAN connection succeeded!') break# Post an Event to the Wia clouddef post_location(latitude, longitude): try: url = "https://api.wia.io/v1/locations" headers = {"Authorization": "Bearer " + DEVICE_SECRET_KEY, "Content-Type": "application/json"} json_data = {"latitude": str(latitude), "longitude": str(longitude)} if json_data is not None: req = requests.post(url=url, headers=headers, json=json_data) if req.status_code is not 200: machine.reset() else: print(json_data) return req.json() else: pass except: passlat = 53lng = -6# main loopwhile True: # Get coordinates from pytrack coord = gps.coordinates(debug=True) if not coord == (None, None): lat, lng = coord post_location(lat, lng) time.sleep(2)Replace the following values of the following variables:
WIFI_SSIDwith your WiFi network name.WIFI_KEYwith your WiFi network password.DEVICE_SECRET_KEYwith your device secret key from earlier (the one that begins withd_sk).
Note: You also need to add pycoproc.py to the lib folder which can be found here
/pycoproc/pycoproc.py)
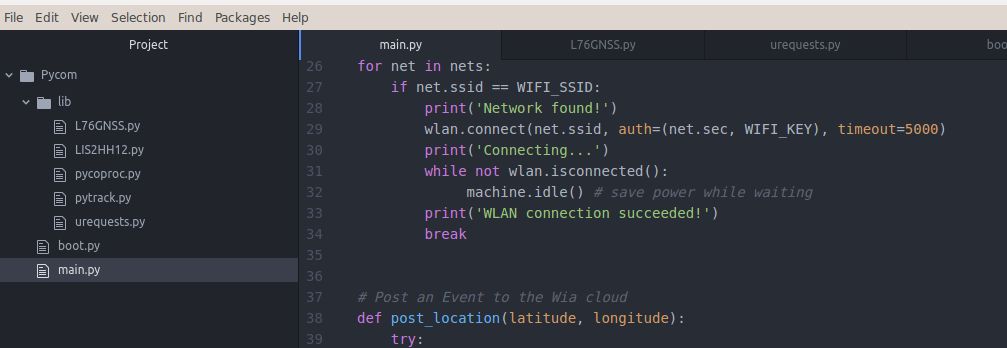
Your folder structure should now look like this:
libL76GNSS.pyLIS2HH12.pypycoproc.pypytrack.pyurequests.pyboot.pymain.py
Click Upload in the Pymakr plugin at the bottom of your window in Atom and send the code to your Pycom board. Now go to the Wia dashboard and you should see it appearing in your device overview.
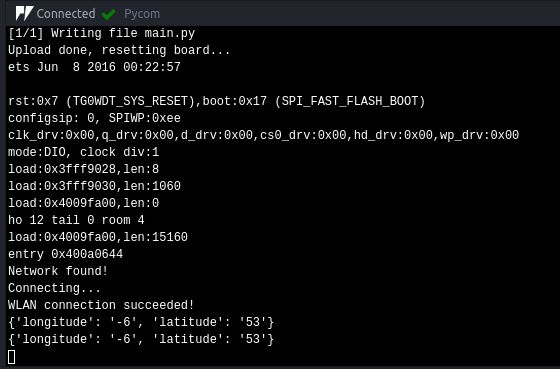
You may need to take your Pytrack outdoors to get a reading for latitude/longitude